Defining Characteristics of Solutions
When we talk about solutions, we're referring to a specific type of mixture where one substance dissolves seamlessly into another. Think of it like this: imagine stirring sugar into your morning coffee. Once the sugar dissolves, the sweetness is evenly distributed throughout the drink. That's what makes a solution so special—it's uniform throughout, meaning the composition and properties are the same no matter where you sample it from.
Uniformity: The Key to Solutions
So, what exactly does it mean for a solution to be uniform? Picture this: you're sipping on a glass of perfectly mixed lemonade. Whether you take a sip from the top, middle, or bottom, the taste is consistent. That's because the solute (the substance being dissolved, like sugar or salt) is evenly distributed within the solvent (the substance doing the dissolving, like water). This even distribution ensures that every part of the solution is identical in composition and properties.
Physical States of Solutions
Here's something interesting: the physical state of a solution—whether it's solid, liquid, or gas—typically matches the state of the solvent. For instance, if you dissolve sugar in water, the resulting solution is a liquid because water is a liquid. Similarly, if you mix gases like oxygen and nitrogen, the solution will also be a gas. This principle holds true across various examples, as you'll see in the table below.
Read also:Unveiling The Truth About Videos Gore A Deep Dive Into The World Of Shocking Content
Examples of Solutions in Everyday Life
Let's dive into some real-world examples to make this concept crystal clear. Think about your favorite perfume. It's a solution of fragrant oils dissolved in alcohol, creating a uniform mixture that smells the same every time you spritz it. Or consider cough syrup, where medicinal compounds are dissolved in a liquid base to ensure the same dose with every spoonful. Other examples include saltwater, sugar water, and even the air we breathe, which is a solution of various gases.
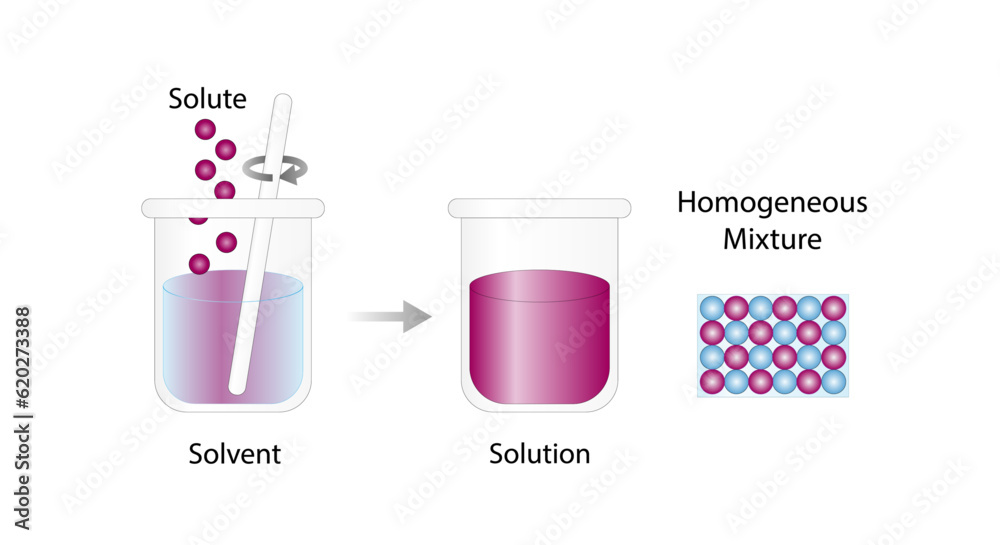
Homogeneous Mixtures: The Science Behind Solutions
In chemistry, a solution is classified as a homogeneous mixture. What does that mean? Simply put, it's a blend of two or more substances that are uniformly distributed throughout. Unlike heterogeneous mixtures, where you can see distinct phases (like oil and water), solutions are seamless and consistent. This uniformity is what sets solutions apart and makes them so useful in everyday life.
What Makes Solutions Uniform?
So, how do solutions achieve this remarkable uniformity? It all comes down to the way the solute and solvent interact. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, the particles of the solute spread out evenly among the particles of the solvent. This process continues until the solute is completely dispersed, creating a consistent mixture. No matter how much or how little of the solution you take, the ratio of solute to solvent remains the same.
Common Misconceptions About Solutions
It's easy to confuse solutions with other types of mixtures, but there are key differences. For example, a mixture of sand and water is not a solution because the sand doesn't dissolve in the water. Instead, it settles at the bottom, creating distinct layers. On the other hand, when you dissolve salt in water, the salt particles spread evenly throughout the liquid, forming a uniform solution. This distinction is crucial in understanding the nature of solutions.
Applications of Solutions in Science and Everyday Life
Solutions aren't just fascinating from a scientific perspective—they also play a vital role in our daily lives. From the beverages we drink to the medications we take, solutions are everywhere. In chemistry labs, solutions are used to conduct experiments and analyze substances. In industries, they're used in everything from manufacturing processes to cleaning agents. Even our bodies rely on solutions to function properly—think of blood plasma, which carries nutrients and waste products throughout the body.
Uniform Distribution: A Closer Look
Let's take a moment to explore the concept of uniform distribution in solutions. Imagine you're baking a cake and need to mix flour and sugar evenly. If the sugar clumps together, your cake won't turn out right. The same principle applies to solutions. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, it spreads out uniformly, ensuring that every part of the solution has the same concentration. This uniformity is essential for the solution to function effectively, whether it's a chemical reaction or a household cleaner.
Read also:26410264691239839135213311243422793123601242738761260323034012394307403135032773653061252412452125211253912454124511246412473123982536125126
Uniform Series Compound Amount Factor: What Does It Mean?
Now, let's shift gears and talk about the uniform series compound amount factor. This concept is often used in finance and engineering to calculate the future value of a series of equal payments. While it may sound unrelated to solutions, the principle of uniformity is similar. Just as a solution maintains a consistent composition throughout, a uniform series ensures that each payment is the same, creating a predictable and reliable outcome.
Conclusion: Why Solutions Matter
In conclusion, solutions are more than just mixtures—they're uniform, consistent, and incredibly useful in both science and everyday life. Whether you're sipping on a glass of lemonade or conducting a complex experiment in a lab, solutions are at the heart of many processes. By understanding their properties and characteristics, we can appreciate the beauty and importance of these remarkable mixtures.
Further Reading and Resources
If you're eager to learn more about solutions and their applications, there are plenty of resources available. From textbooks and online courses to hands-on experiments, the world of solutions is vast and fascinating. So, grab a cup of coffee (a solution, by the way), and dive into the wonderful world of chemistry!